Yellow Tail vineyard sale
Australian producer and the world's most recognisable wine brand is planning on selling their 7258ha of vineyards in Australia. Read more »
BOOKINGS: 020 8288 0314
Cabernet Sauvignon is perhaps the most famous red grape. Its home is Bordeaux where it is was created as a cross between Cabernet Franc (red grape) and Sauvignon Blanc (white grape). Since then its popularity has spread and it is grown all around the world. It prefers warmer climates to ripen fully and even in Bordeaux some years it does not ripen. That is why Cabernet Franc is also used in Bordeaux blends as it ripens faster. What makes Cabernet so popular is not its bouquet, which can range from blackcurrants to cigar box, but its structure, typically having both tannins and acidity to create a smooth feeling in the mouth. The structure allows the blending with other grapes, perhaps the most famous pairing is Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot where the Cabernet provides the structure and the Merlot gives the wine the soft, rounded feel in the mouth. Recently Cabernet has been mixed with Sangiovese (Chianti's grape) to create the SuperTuscans.
Jancis Robinson described Chardonnay as the tart of the grape world, as it would lie down anywhere and do what the winemaker told it to do! In other words it will grow almost anywhere and produce decent and quite stylistically different wines ranging from minerally Chablis, Champagne, buttery fruit wines, tropical fruit wines or oaky vanilla wines. During the late 1990's Chardonnay was the drink of choice for many. However people became bored with the oaky wines found in so many bars and the term, 'ABC' (Anything but Chardonnay) came about. The ubiquitous yet noble Chardonnay grape has virtually become a brand name. From its homeland in Burgundy, its fame and fortune have taken it all over the world. It�s grown on different soils in varying climates to be used either as a single varietal or in blends, for still and sparkling wines, and with or without oak ageing to create a wide range of wines with diverse personalities. As a result, it�s impossible to describe a typical Chardonnay. For a start, the grape can make anything from an everyday glugger to a high-quality wine deserved of ageing. Its popularity in the vineyard stems from the fact that it�s easy to grow, consistently yielding generously with relatively high sugars (and, therefore, alcohol). In the winery its advantages are obvious � it�s difficult to make a poor wine from it, unless it�s been picked too late, because then its acid levels fall quickly, which make it flabby. Chardonnay isn�t strongly aromatic: some detect anything from apples (or barely ripe apples in Chablis) and melon in Maconnais Chardonnay to tropical fruit flavours in New World examples. Common descriptives, however, tend to refer to texture and weight rather than flavour � buttery for broader styles, such as Meursault from the Cote de Beaune; steely for Montrachets and nutty for Corton-Charlemagne. There�s an attractive leanness to fine Cote d�Or white burgundy, that sets it apart from Chardonnays from the rest of the world, but this can be emulated further south in the Cote Chalonnaise and Maconnais in good vintages with clever winemaking.
Wine Regions for New South Wales
Key Grape Varieties: Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay
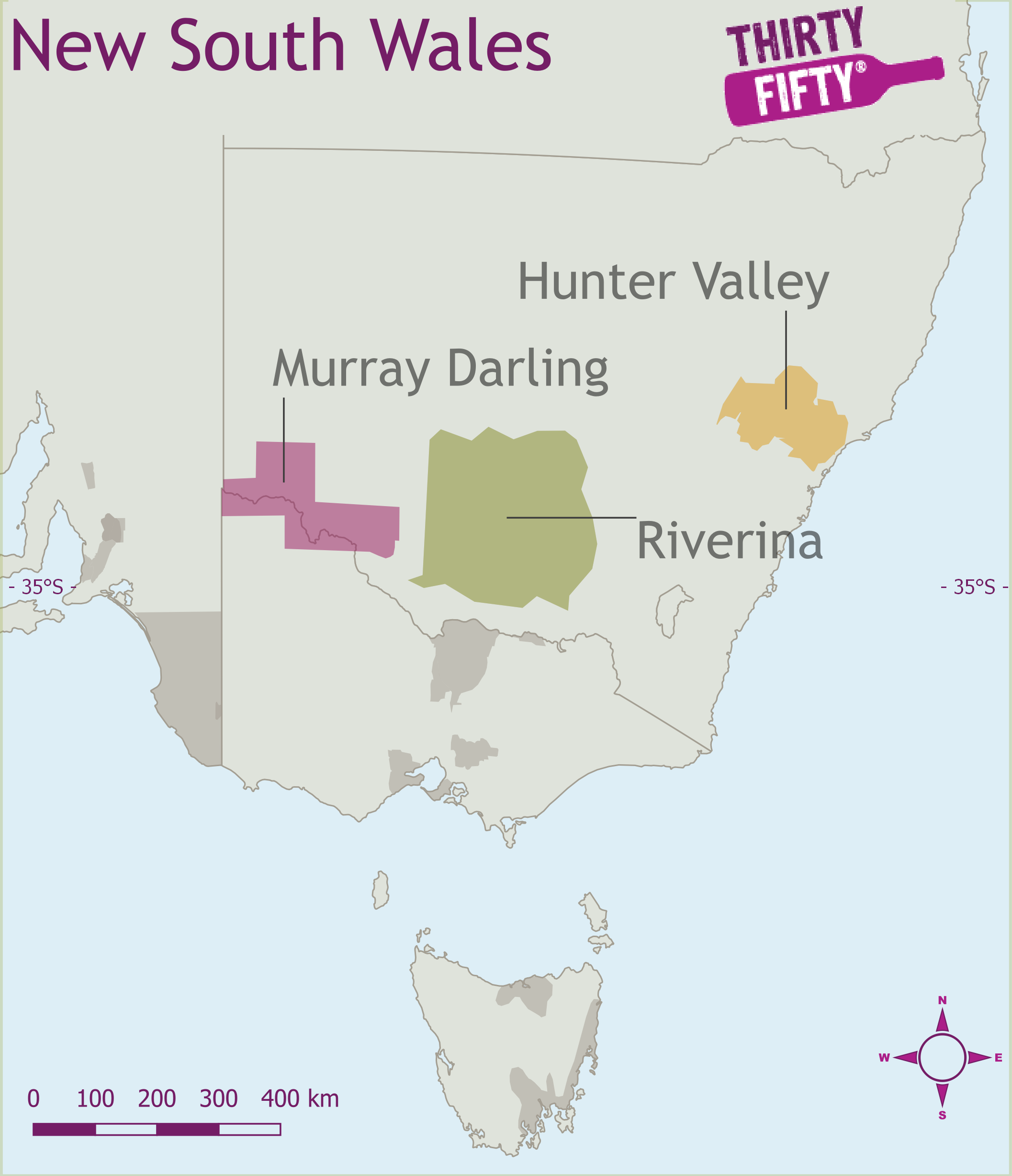
The New South Wales wine region is centered around the sate capital Sydney and into the Great Dividing range. Starting in the North Hunter Valley and going south, The Hunter provides excellent examples of age worthy Semillion, while Mudge Orange Cowra, Hilltops Canberra district and Tumarumba, provide a range of cooler climates from the altitude of the great diving range.
The New South Wales wine region is centered around the sate capital Sydney and into the Great Dividing range. Starting in the North Hunter Valley and going south, The Hunter provides excellent examples of age worthy Semillion, while Mudge Orange Cowra, Hilltops Canberra district and Tumarumba, provide a range of cooler climates from the altitude of the great diving range.
The lesser known coastal regions of Hastings River, Southern Highlands and Shoalhaven Coast produce a tiny fraction of New South Wales inland engine room of Riverina, Swan Hill and Murray Darling.